Semipermeable membrane

A semipermeable membrane, also termed a selectively-permeable membrane, a partially-permeable membrane or a differentially-permeable membrane, is a membrane that will allow certain molecules or ions to pass through it by diffusion and occasionally specialized "facilitated diffusion."
The rate of passage depends on the pressure, concentration, and temperature of the molecules or solutes on either side, as well as the permeability of the membrane to each solute. Depending on the membrane and the solute, permeability may depend on solute size, solubility, properties, or chemistry. How the membrane is constructed to be selective in its permeability will determine the rate and the permeability.
An example of a semi-permeable membrane is the lipid bilayer, on which is based the plasma membrane that surrounds all biological cells. Many natural and synthetic materials thicker than a membrane are also semipermeable. One example of this is the thin film on the inside of an egg.
Another example of a semipermeable membrane which is very specific in its permeability is a phospholipid bilayer, a group of phospholipids (consisting of a phosphate head and two fatty acid tails) arranged into a double-layer. The hydrophilic phosphate heads are in the outside layer and exposed to the water content outside and within the cell. The hydrophobic tails are the layer hidden in the inside of the membrane. The phospholipid bilayer is the most permeable to small, uncharged solutes. Protein channels float through the phospholipids, and, collectively, this model is known as the fluid mosaic model.
In the process of reverse osmosis, thin film composite membranes (TFC or TFM) are used. These are semipermeable membranes manufactured principally for use in water purification or desalination systems. They also have use in chemical applications such as batteries and fuel cells. In essence, a TFC material is a molecular sieve constructed in the form of a film from two or more layered materials.
Membranes used in reverse osmosis are, in general, made out of polyimide, chosen primarily for its permeability to water and relative impermeability to various dissolved impurities including salt ions and other small molecules that cannot be filtered. Another example of a semipermeable membrane is dialysis tubing.
Other types are cellulose ester membrane (CEM), charge mosaic membrane (CMM), bipolar membrane (BPM), anion exchange membrane (AEM)[1] alkali anion exchange membrane (AAEM) and proton exchange membrane (PEM).
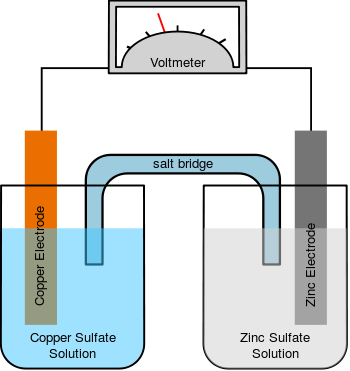
Osmosis is the diffusion of a substance through a selectively permeable membrane.
See also
- ADME
- Artificial membrane
- Barrer
- Osmosis
- Reverse osmosis
- Diffusion
References
External links
- EuroMemHouse - European Membrane House
- Membrane terminology. International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry recommendations.
|
||||||||||||||||
| This biochemistry article is a stub. You can help Wikipedia by expanding it. |